Process Street‘s Code Tasks provide powerful automation capabilities by executing JavaScript within workflows.
Whether calculating costs, extracting data, setting task priorities, or defining unique business logic, this feature is useful for performing complex operations beyond standard workflow automation.
You can use these tasks to perform multi-step calculations and make API calls to calculate data from another tool within your workflows. This reduces the need for reliance on third-party tools to perform calculations for you.
Users: In order to add or change Code Tasks in a workflow, you must be an Administrator or a Member who has been given ‘edit’ access by your Administrator.
Code Task is automatically available on our Enterprise plan. Please contact our Support team or your Account Executive to inquire about access.
Here are just a few examples of how you can utilize Code Tasks, but the limits are really your imagination!
You can create Code Tasks in an existing workflow where you already have form fields created, or in a new workflow that you start from scratch.
If you’re starting from scratch, consider which input and output form fields you might want to include as part of your Code Task.
In your workflow click the + button at the end of the task list to add a Code Task.
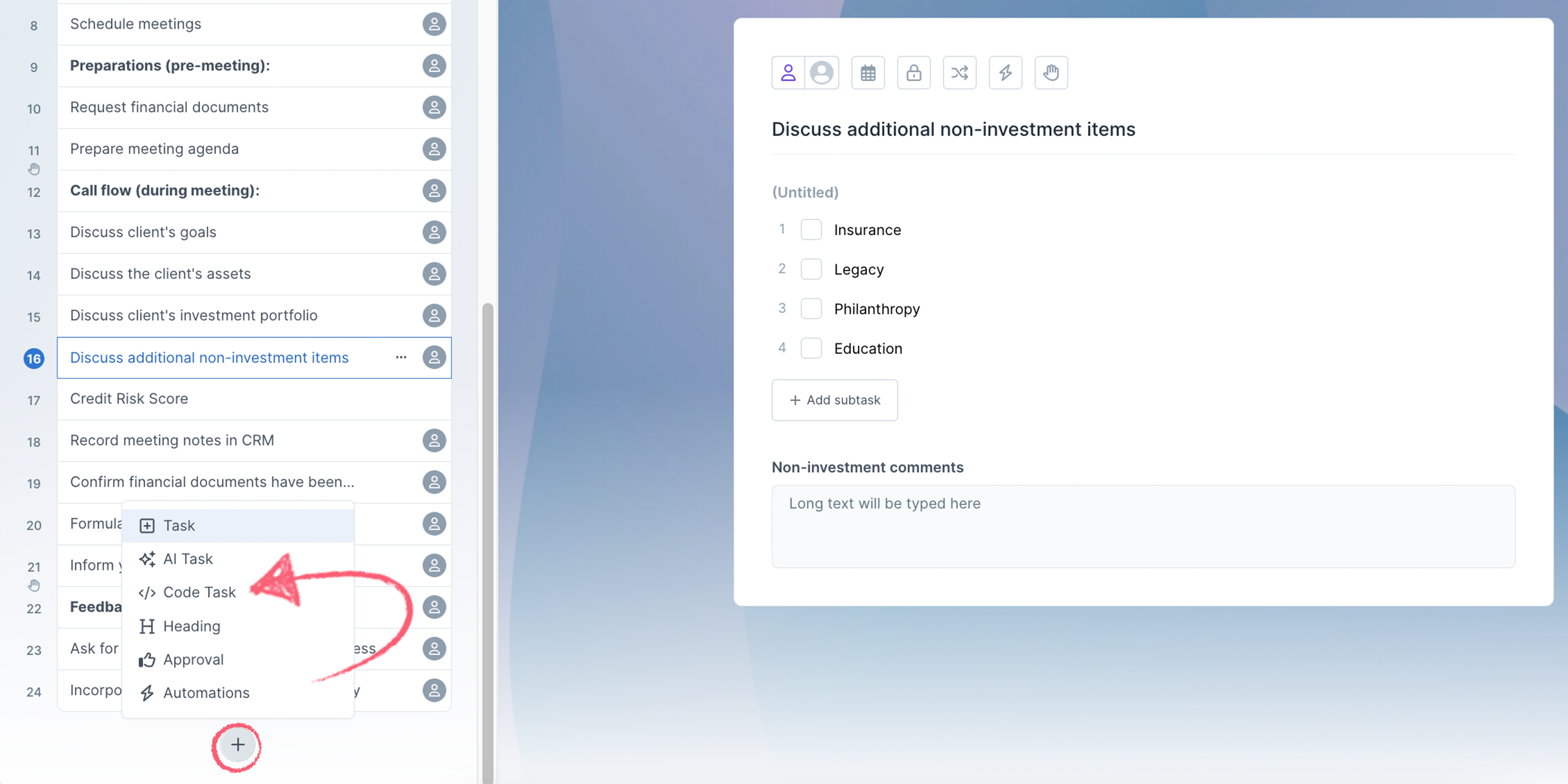
Click the dropdown shown in the image below to select a prebuilt function.

Under the Input data section, click + Add value to add more input fields, or use the trash can to delete the ones you don’t need.
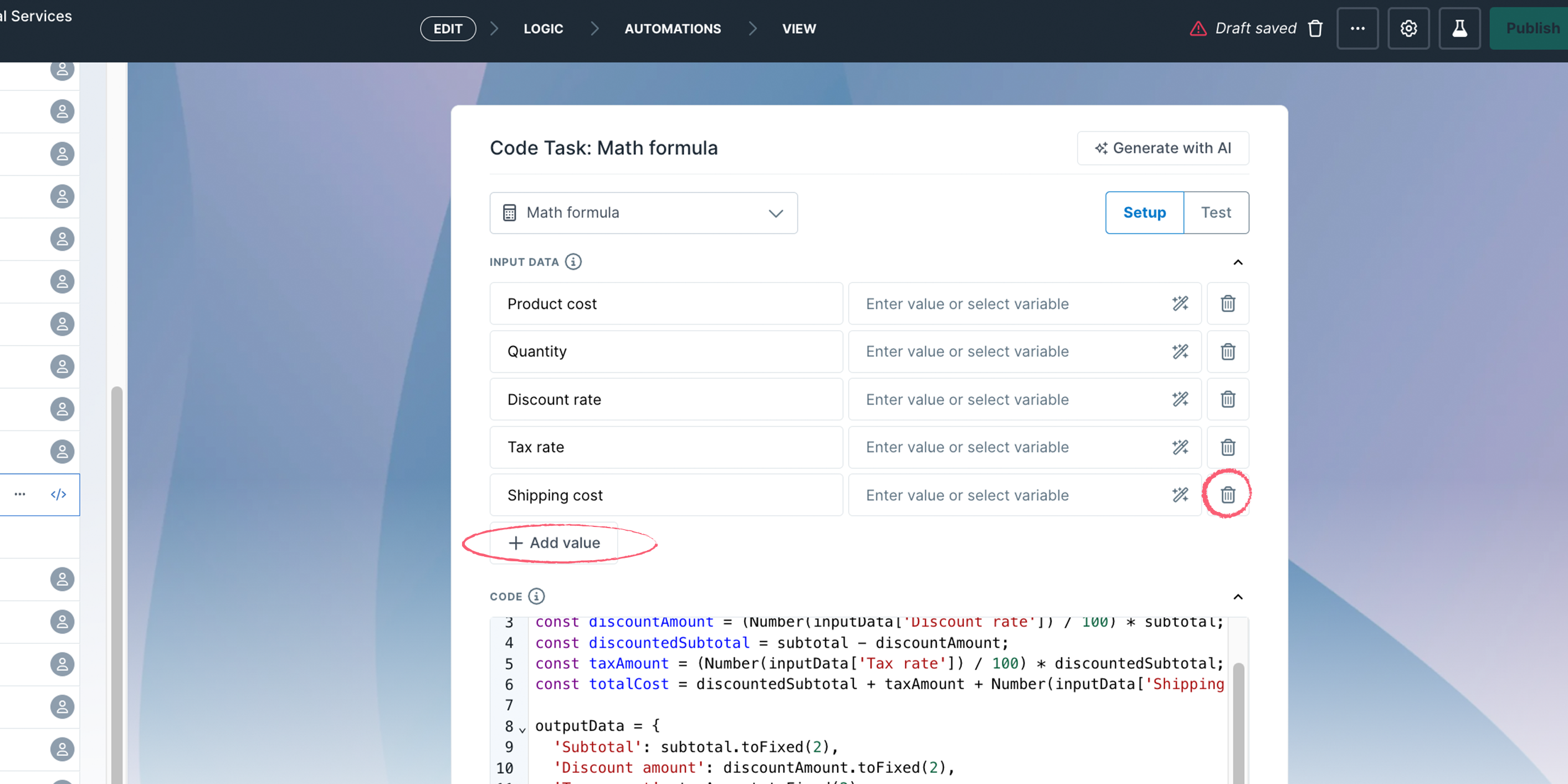
These values can be manually entered or pulled from previous workflow tasks as variables. A manually entered value for the API call would be your API key, for example.
Input form fields you can use are:
Output form fields you can use are:
Note: In workflow view mode, other users won’t see API keys or other static values in your input fields unless they have edit permission on the workflow or they are an admin.
Click Generate with AI to let our Process AI wizard create the code for you.
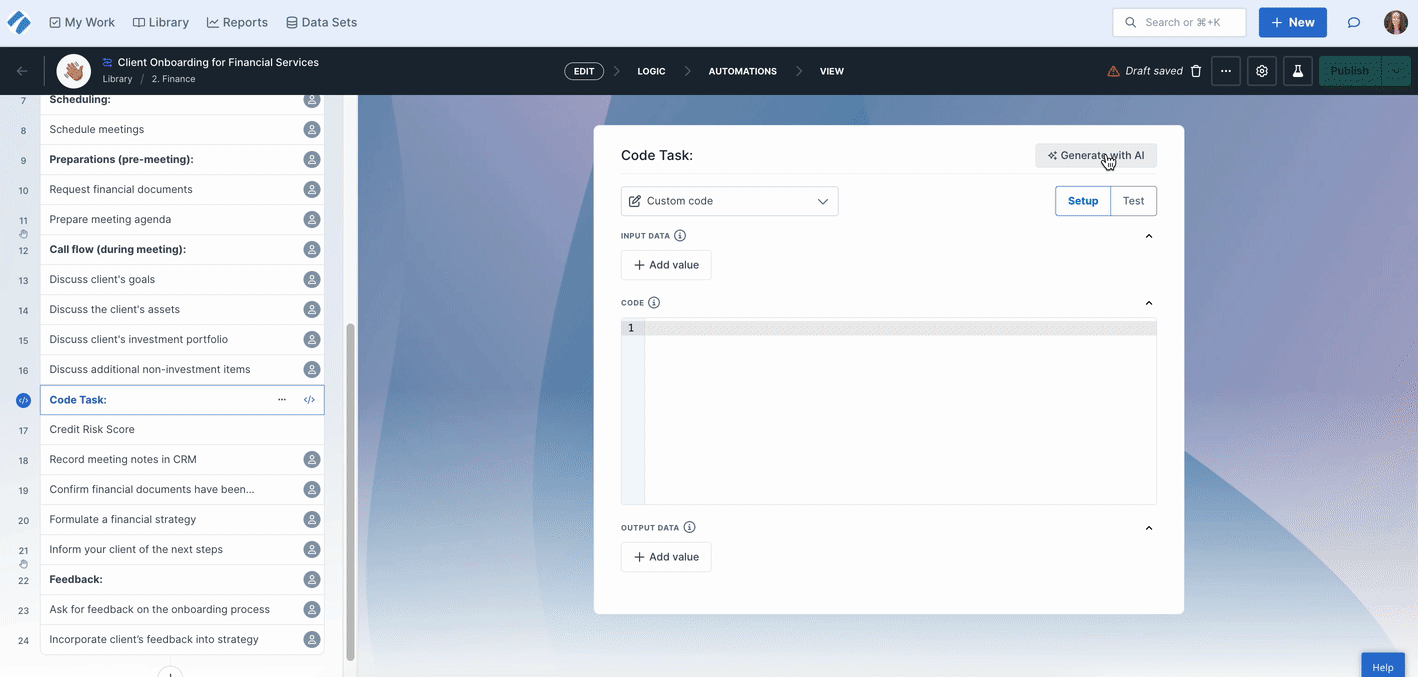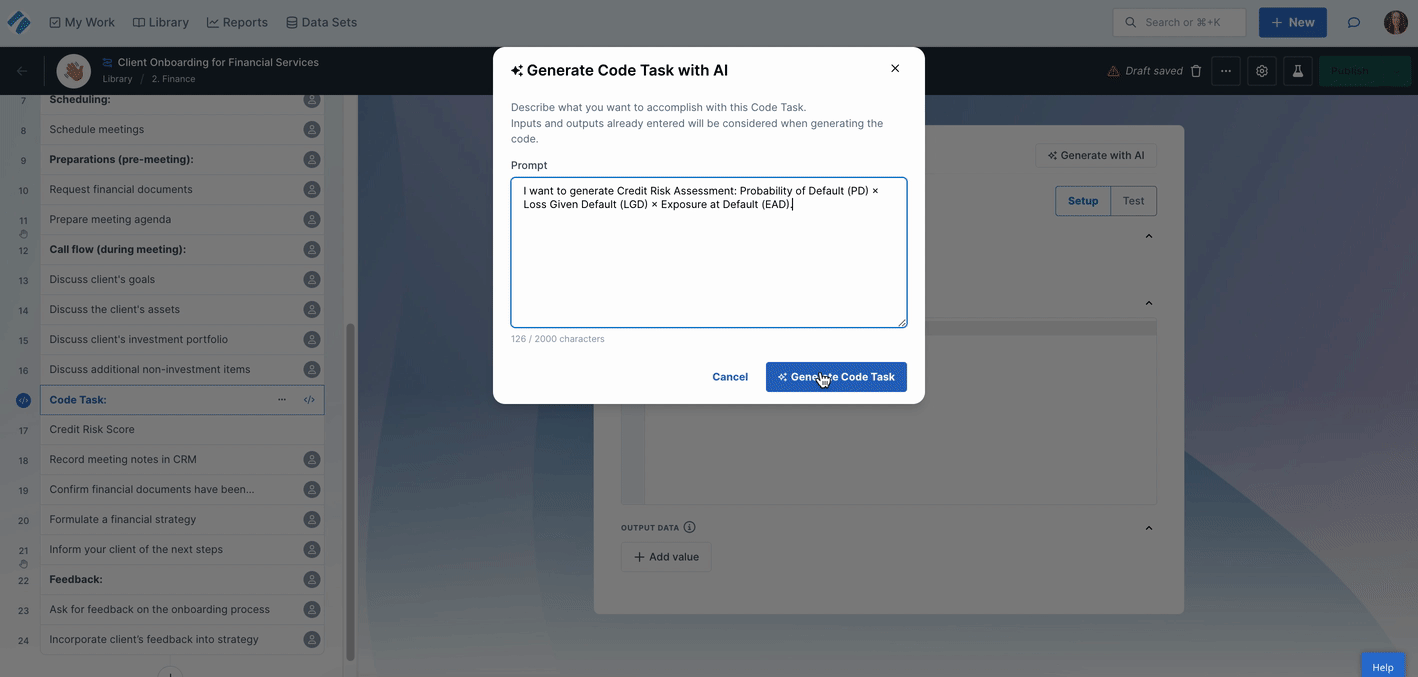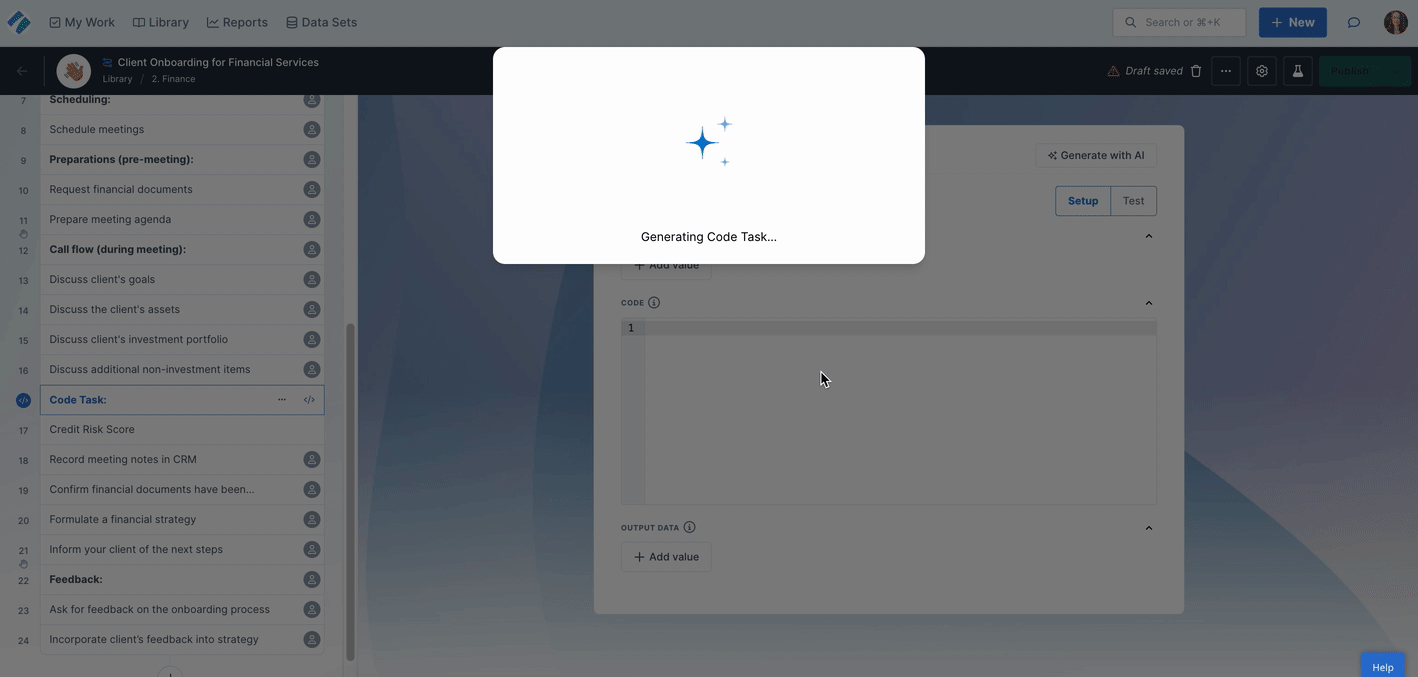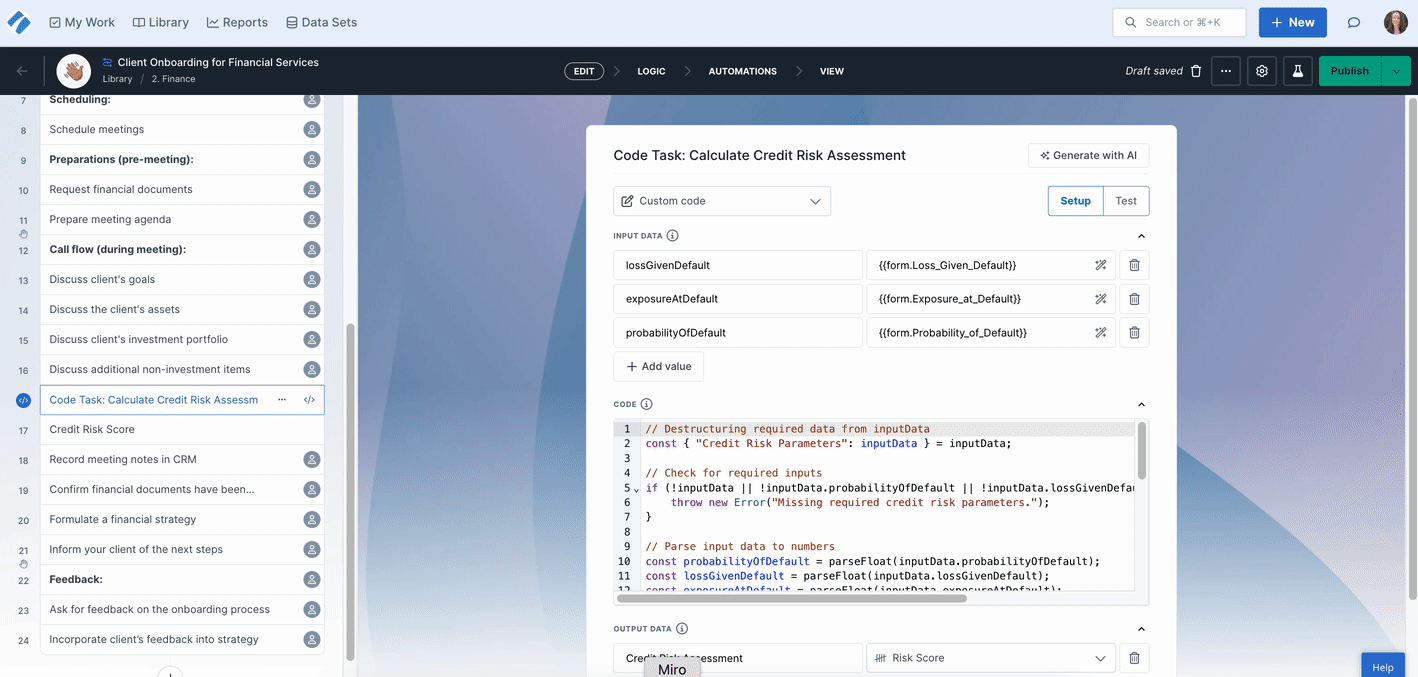
Simply write a prompt and the Code Task looks at your existing input and output form fields and adds these in for you, ready for testing.
If you’re already familiar with JavaScript and don’t need presets or AI generation, you can write and execute fully custom JavaScript logic.
Input fields can be accessed by reading keys of the inputData variable and 0utput fields can be written by setting keys of the ouputData variable.
Example: The Code Task has an input called “Customer Name” and an output called “Address”. They can be accessed in the following way:
const customerName = inputData[“Customer Name”]
outputData[“Address”] = “599 Broadway, New York, 10012”
When you’re done setting up your inputs, outputs and code, you can go ahead and test it.
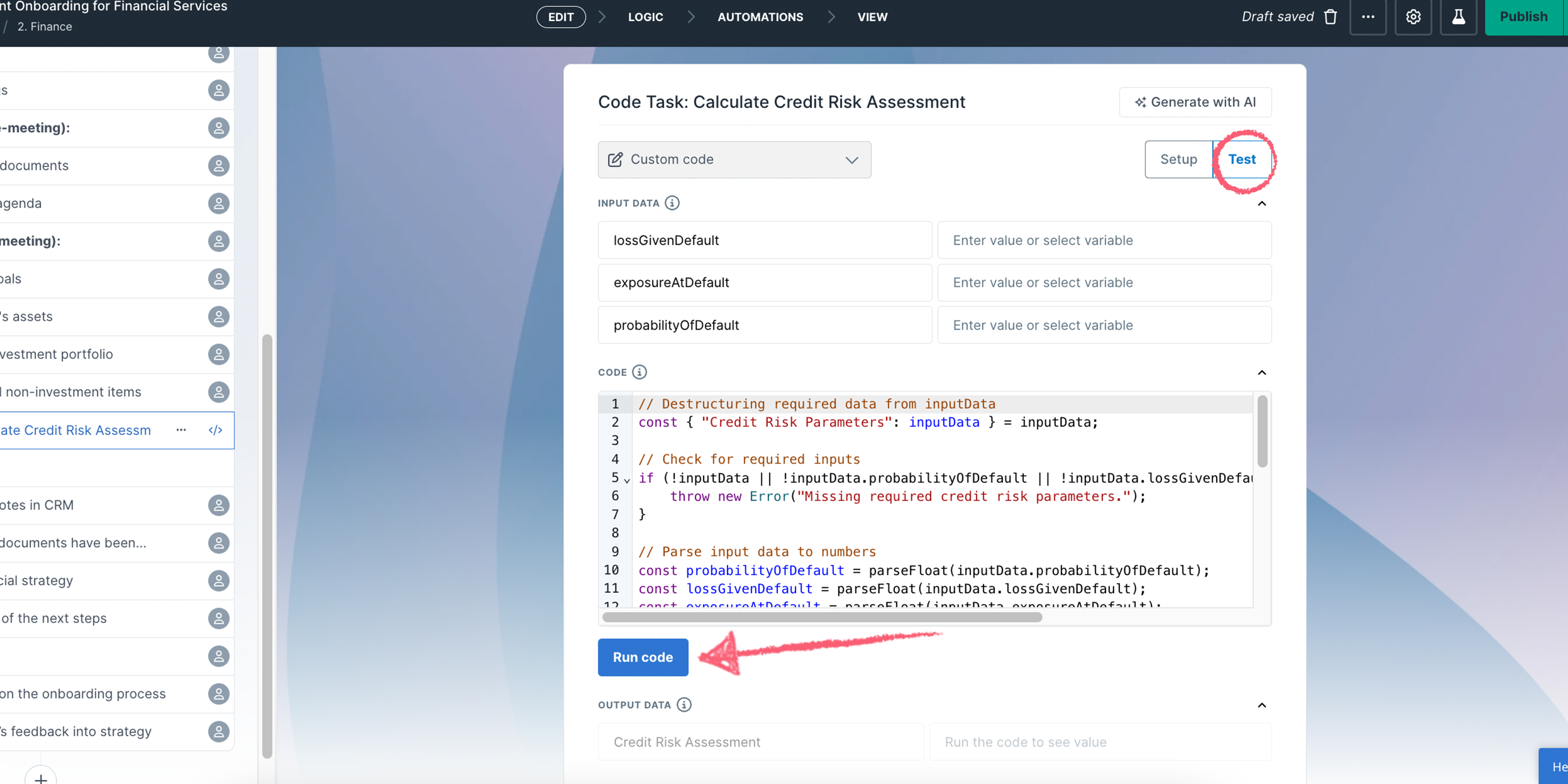
At this point you can go ahead and preview the Code Task in the editor, or publish it ready to be used.
Note: If you require longer than 5 seconds per execution, please contact our Support team or your Account Executive.
What happens if my script exceeds the limits?
If a script exceeds execution time or memory limits, it will be terminated, and an error will be returned.
Can I make API calls within a Code Task?
Yes, but keep in mind the execution time limit (5 seconds) when making network requests.
What version of Node.js does Process Street use?
Code Tasks run on Node.js 22.
Are there any rate limits?
Currently, no rate limits apply.
Can I use third-party libraries?
At the moment, only native Javascript functions are supported – external libraries cannot be imported. See the list below for allowed globals.
How do I debug my Code Task?
Use the Test feature to run the code and review the output. Debugging logs can be added using console.log().
What timezone do Code Tasks use?
-All date/time operations in Code Tasks follow UTC timezone, regardless of account settings.
Where can I get support?
For advanced JavaScript issues, consult a developer.
Process Street provides support for how the Code Task processes code but does not debug user scripts.
All standard Javascript built-in objects are available (e.g. Math, Date, RegExp). Moreover, we have allowlisted the following Node.js globals:
“Blob”,
“Buffer”,
“console”,
“crypto”,
“fetch”,
“FormData”,
“Headers”,
“Request”,
“Response”,
“URL”,
“URLSearchParams”,
“clearInterval”,
“clearTimeout”,
“setInterval”,
“setTimeout”,
“structuredClone”